Ten Remarkable Milestones Celebrating 100 Years of Modern Banking in Mongolia
1. Inflation remained within the central bank’s target range throughout the year
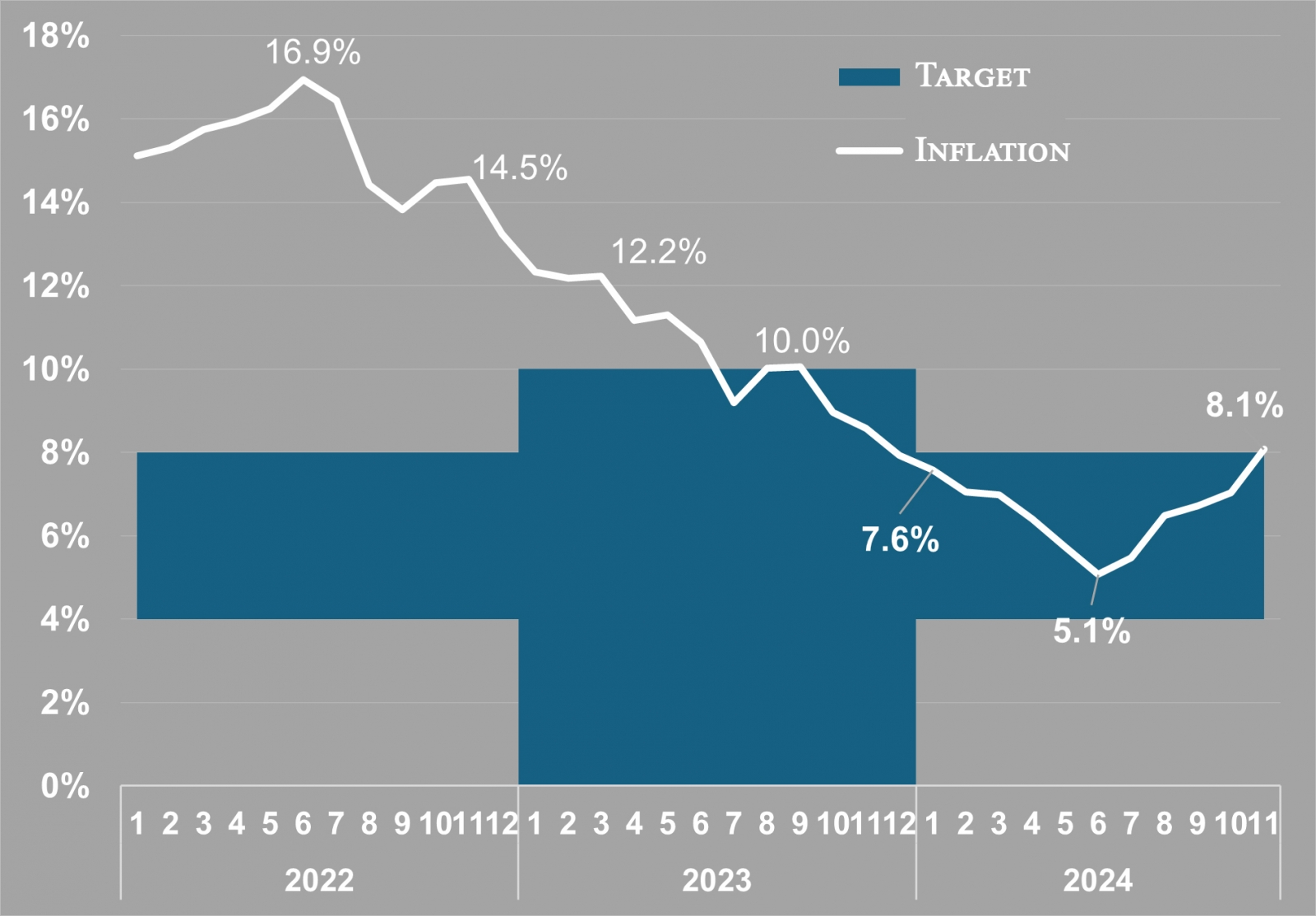
In 2024, inflation, a primary objective of the central bank, was successfully brought down within the Bank of Mongolia’s target range. Despite ongoing challenges stemming from the global pandemic and Russia-Ukraine war, including external uncertainties and disruptions in transport and logistics, inflation averaged 6.6 percent for the year. However, inflationary pressures persist, driven by factors such as increased government spending, credit and wage growth, rising electricity and heating costs, and the impact of two consecutive years of dzud. Moving forward, monetary policy will focus on addressing these pressures to ensure inflation remains within the target range.
2. Foreign exchange reserves reach a historic high of $5.5 billion
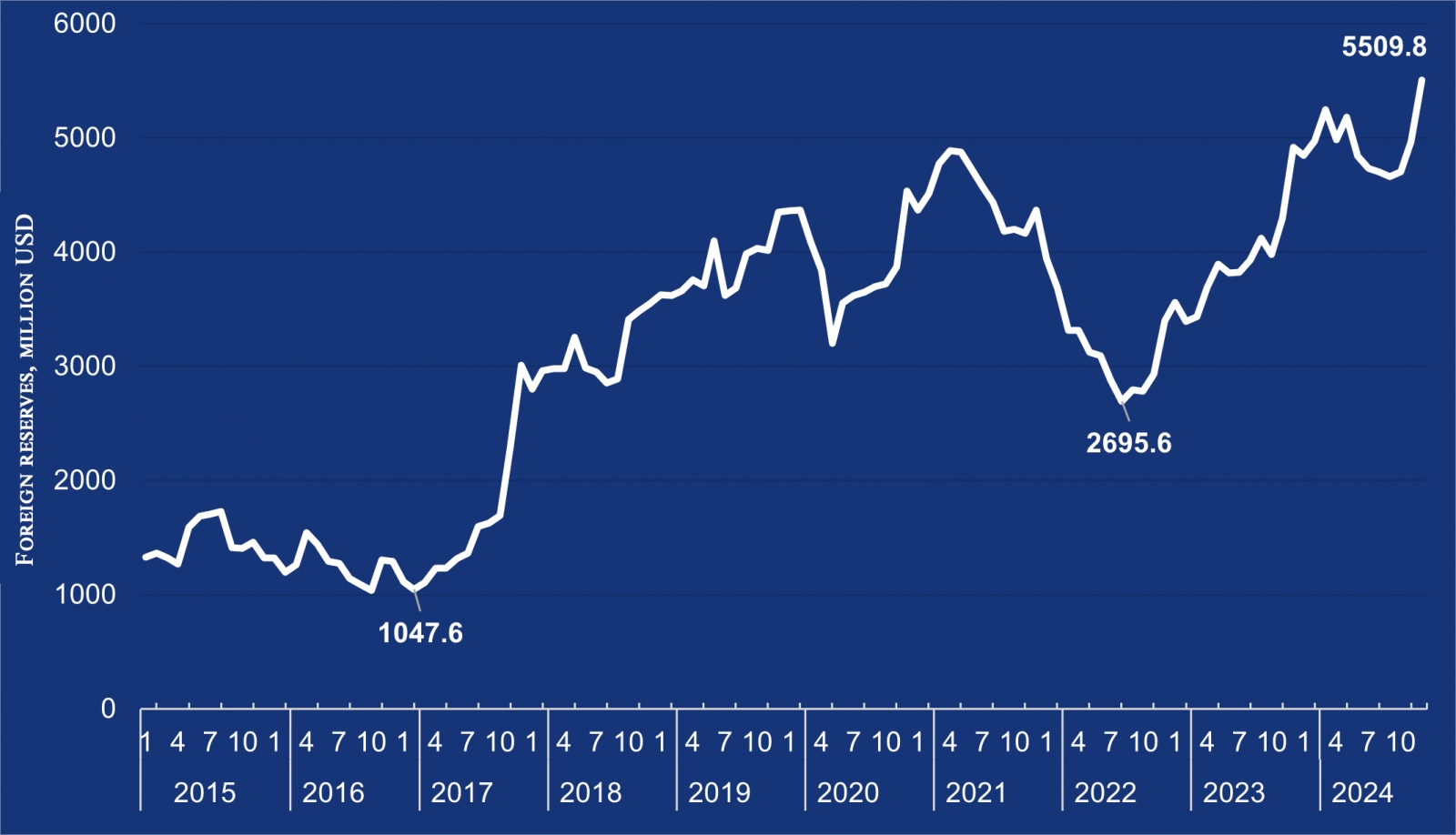
Foreign exchange reserves reached a record high of USD 5.5 billion by the end of 2024. This achievement reflects the effectiveness of macroeconomic policies, a boost in investor confidence in Mongolia, increased foreign financing, and higher export earnings.
The year-end reserve level is particularly noteworthy, as it was achieved despite substantial external debt repayments. In 2024, the Bank of Mongolia repaid a net total of USD 450 million in government foreign loans and bonds, along with RMB 4.5 billion under the swap agreement with the People's Bank of China. These repayments, amounting to approximately USD 1.1 billion in principal and interest, underscore the resilience of Mongolia's foreign reserve position.
3. Mongolia’s sovereign credit rating upgraded to the highest levels in a decade
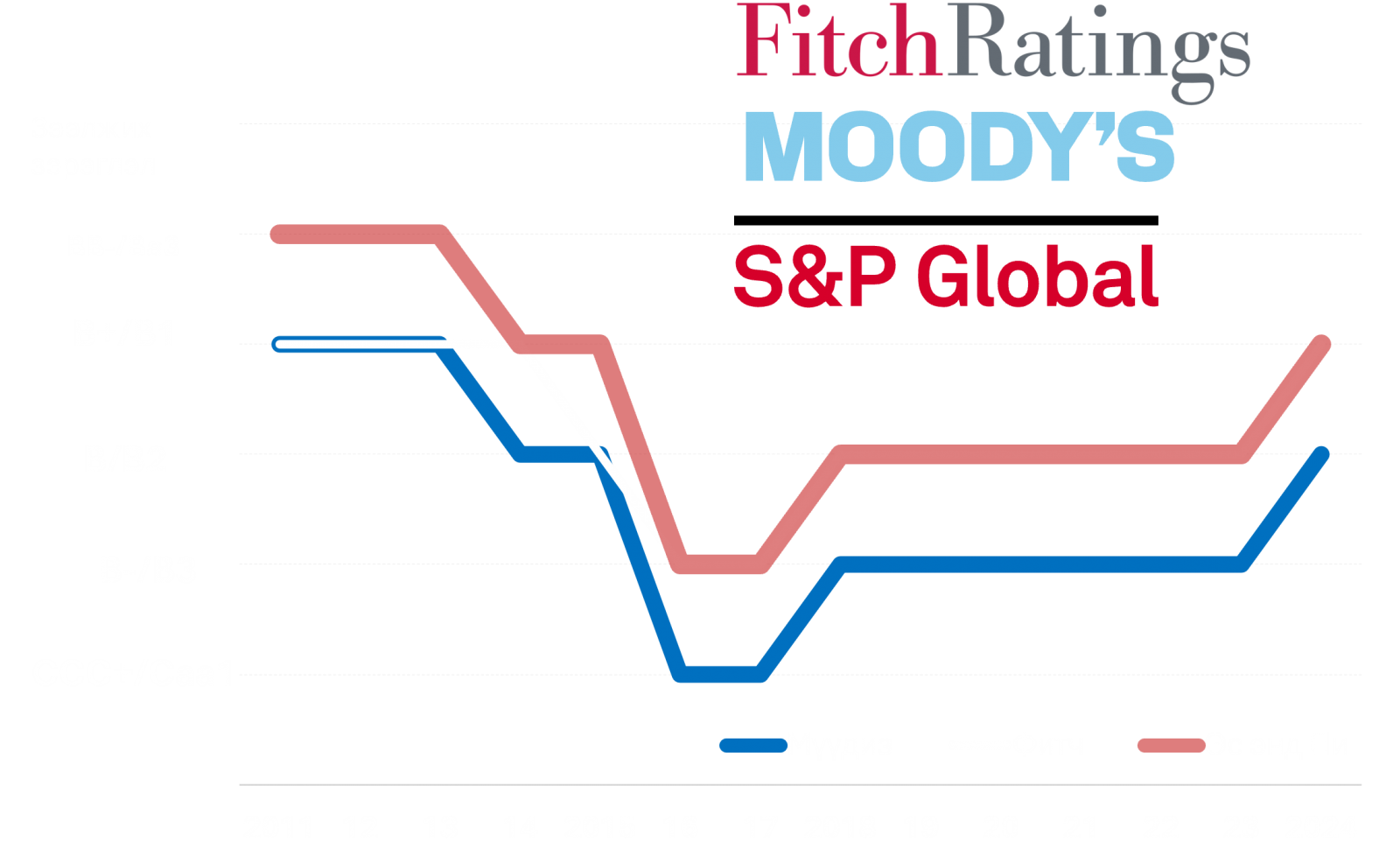
In 2024, international credit rating agencies Fitch, S&P, and Moody’s upgraded Mongolia’s sovereign credit ratings to “B+,” “B+,” and “B2,” respectively—the highest levels in a decade. These upgrades reflect positive assessments of the policies implemented by the Mongolian Government and the Bank of Mongolia, as well as renewed investor confidence and optimistic economic outlooks.
The improved credit ratings highlight Mongolia’s enhanced macroeconomic stability, declining inflation, accelerated economic growth, and effective external debt management. This development is particularly significant for strengthening Mongolia’s ability to secure financing on more favourable terms in international financial markets.
For instance, in recent months, Mongolian commercial banks successfully issued USD 350 million worth of bonds on the international market at lower interest rates than previous transactions, demonstrating increased market confidence.
3. Swap agreement balance between People’s Bank of China and Bank of Mongolia halved

The Bank of Mongolia has repaid 4.5 billion yuan in principal and interest ahead of schedule, reducing the outstanding balance of the Bilateral Local Currency Swap Supplemental Agreement with the People's Bank of China to 6 billion yuan. This move has effectively halved the Central Bank’s reliance on foreign swap agreements, resulting in a significant reduction in interest expenses and a notable increase in net foreign exchange reserves. Consequently, Mongolia's external debt stability has been reinforced, contributing to an improved long-term credit rating. These developments have bolstered investor confidence and enhanced the country’s overall financial resilience.
5. Apple Pay launches in Mongolia

Efforts to introduce cutting-edge payment technologies aligned with international best practices in Mongolia are ongoing. On December 10, 2024, "Apple Pay" was officially launched, enabling Mongolian consumers to make payments using their iPhones at over 150,000 POS terminals across the country. This development also paves the way for the national payment card, the “₮ card,” to be utilized for international transactions, marking a significant step forward in modernizing Mongolia's payment systems.
6. International high-level conference on “Modern Central Banking: Challenges and Prospects” held in Ulaanbaatar

The Bank of Mongolia and the Mongolian Banking Association, in collaboration with international financial institutions, organized a high-level international conference titled “Modern Central Banking: Challenges and Prospects” in Ulaanbaatar on July 9–10, 2024. The event brought together over 180 esteemed guests, researchers, and policymakers from 62 international and domestic organizations. Participants engaged in discussions on the future prospects of global and regional economies, financial markets, and the key challenges and solutions facing central banks today.
7. APG Annual Meeting commends Mongolia's efforts to combat money laundering
At the opening of the APG (Asia-Pacific Group on Money Laundering) Annual Meeting, held in the United Arab Emirates in September 2024, the Group’s Chairman highlighted Mongolia’s significant progress. He noted that "Mongolia is the fifth country to fully comply with the FATF’s 40 Recommendations and the second in the Asia-Pacific region to achieve this milestone."
The Chairman commended Mongolia’s proactive approach to engaging with international standards on virtual assets, submitting annual Reassessment Reports, and successfully defending and enhancing its evaluations. He also praised the country’s achievements in combating money laundering, emphasizing that it had completed its required tasks within an unprecedentedly short period of six months, despite the challenging circumstances of the global pandemic.
8. “Global Finance” magazine recognizes the Bank of Mongolia’s leadership
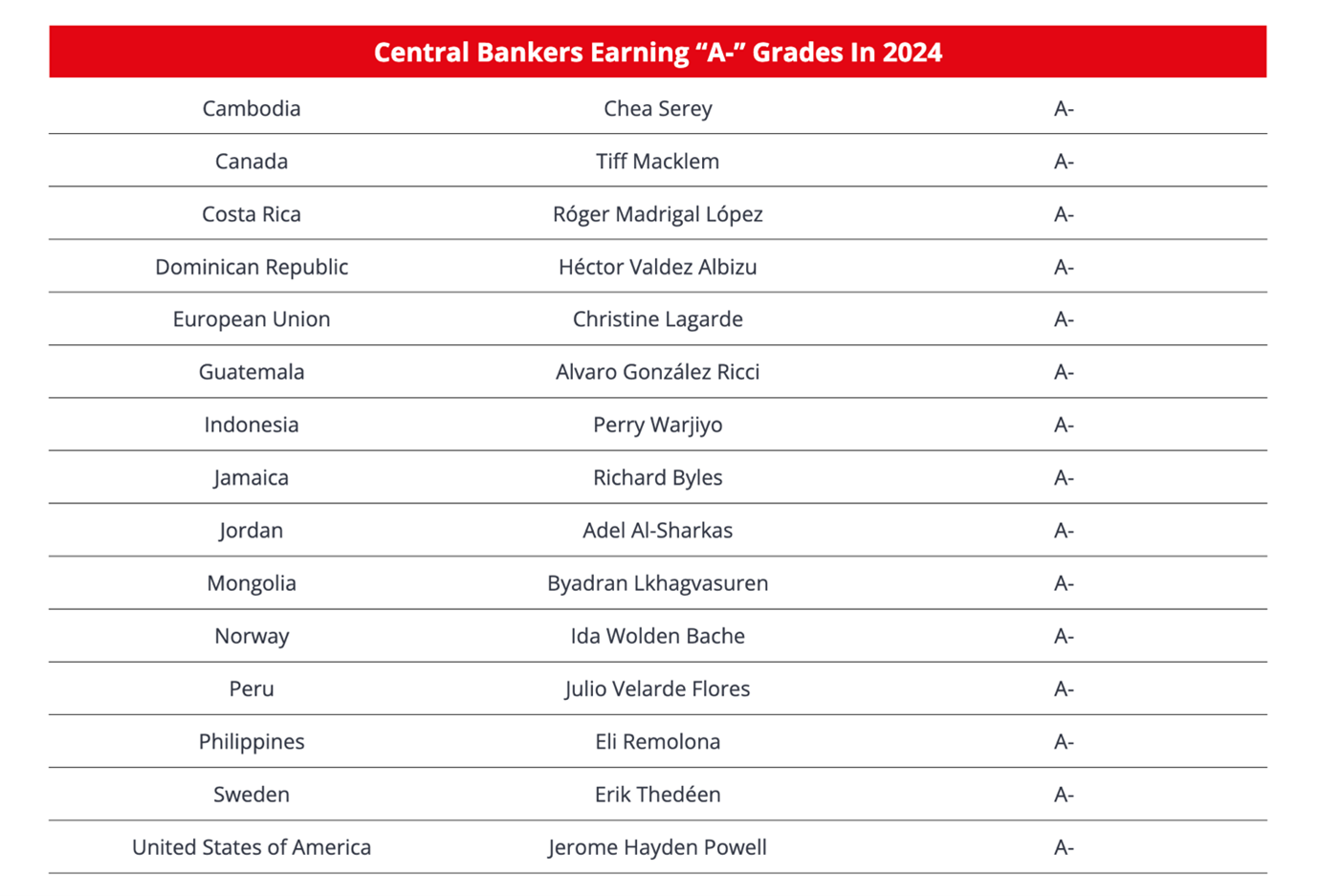
Global Finance magazine has awarded an “A-” rating to B. Lkhagvasuren, Governor of the Bank of Mongolia, in its prestigious Central Banker Report Cards 2024. This rating places Governor Lkhagvasuren alongside prominent central bankers such as Christine Lagarde, President of the European Central Bank, and Jerome Powell, Chairman of the U.S. Federal Reserve. Since its inception in 1994, the Central Banker Report Cards have been a benchmark for evaluating the performance of central banks and their leaders across approximately 100 countries, including the United States, the European Union, and the United Kingdom. The annual assessment, highly regarded by financial professionals, considers key indicators such as the implementation of monetary policy, achievement of inflation targets, support for economic growth, and currency stability. This recognition underscores the Bank of Mongolia's effective leadership and its commitment to maintaining financial and economic stability.
9. Bank of Mongolia actively supports Green Finance Initiatives to combat climate change

This year, the Bank of Mongolia launched the “Readiness Support for Greening the Bank of Mongolia” project, supported by the United Nations (UN) Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) Partnership. As part of this initiative, the Bank is conducting Mongolia's first-ever climate stress test of the banking sector, utilizing quantitative data from systemically important banks. Additionally, climate transparency reporting guidelines have been developed to enhance climate-related disclosures by banks.
Significant advancements have been made in financial data classification, with financial inclusion indicators now categorized by gender equality and green finance. Statistical data has also been enriched to support more robust analysis. Starting in 2024, the Bank of Mongolia will, for the first time, disaggregate and publicly release data on loans, current accounts, deposits, and green loans for micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises, as well as enterprises at the soum, district, and village levels. Green loan reports and sector-specific loan data for the entire financial system will also be made publicly available.
As of the third quarter of 2024, the balance of green loans issued by the banking sector reached MNT 1.2 trillion, representing 3.4 percent of total loans—a remarkable 92.6 percent increase compared to the same period last year. The Bank aims to sustain this growth, targeting a green loan share of 10 percent by 2030.
In celebration of the 100th anniversary of Mongolia's banking system, the Bank of Mongolia, in collaboration with the “Ten Thousand Trees” Foundation and other organizations, has planted over 3 million trees across Ulaanbaatar and all 21 aimags. The Bank is also working with professional organizations to ensure the long-term care and maintenance of these trees, reinforcing its commitment to environmental sustainability alongside its financial initiatives.
10. The resilience of the banking sector has strengthened, serving as a foundation for stable economic growth
The Bank of Mongolia is committed to fulfilling its statutory mandate of supporting the balanced development of the national economy by ensuring the stability of the financial market and the banking sector. As of November 2024, the banking sector exhibited significant growth and resilience. Total assets increased by 5,598.1 billion tugriks, or 9.7 percent; the loan portfolio expanded by 8,428.9 billion tugriks, or 31 percent; and equity grew by 992.1 billion tugriks, or 17 percent, compared to the same period in the previous year. Additionally, the non-performing loan (NPL) ratio decreased to 5.1 percent, the lowest level since 2014. These improvements in the financial performance of the banking sector, combined with a reduction in credit risk, contribute positively to strengthening the sector’s resilience and fostering stable economic growth in the future.
